Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation
Deducing the Link Key, just by passively sniffing the pairing process. Becoming more and more widespread, a secure pairing method became a hard requirement for ensuring the long term success of the technology. Introduced in the 2.1 specification, Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) fixes. Oct 23, 2018 Phase 2 — Pairing Over SMP. After exchanging paring features, phase two is for Long Term Key (LTK) generation. Exploiting Bluetooth Low Energy Pairing Vulnerability in Telemedicine. Exploiting Bluetooth Low Energy Pairing V ulnerability in T. In the Just Works pairing method the key is known, while.
- Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation 2
- Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation Download
- Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation 1
- Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation 3
Key generation is the process of generating keys in cryptography. A key is used to encrypt and decrypt whatever data is being encrypted/decrypted.
Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation 2
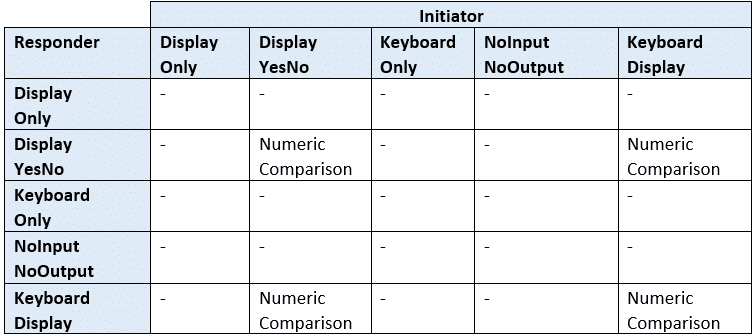
A second contribution is the design of an efficient column generation method for the crew pairing. It leverages in the shortest path framework proposed by the first author 29 to avoid the construction of the duties network 12 and speed-up the resolution of the pricing subproblem. ESS210B Prof. Jin-Yi Yu Significance Test of Correlation Coefficient When the true correlation coefficient is zero (H0: ρ=0 and H1: ρ≠0) Use Student-t to test the significance of r and ν= N-2 degree of freedom When the true correlation coefficient is not expected to be zero We can not use a symmetric normal distribution for the test. Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is a cryptographic system that uses pairs of keys: public keys, which may be disseminated widely, and private keys,which are known only to the owner. The generation of such keys depends on cryptographic algorithms based on mathematical problems to produce one-way functions. Effective security only requires keeping the private key private; the public key. Aug 25, 2016 You generate the STK using the key generation function s1 detailed in the Bluetooth Core Spec V4.2, Vol.3, Part H, Section 2.2.4. For s1 function, the input parameters include: TK; Srand; Mrand; The paired devices establish an encrypted link with STK. In Part 4, I introduce a new pairing algorithm in LE Secure Connection: Numeric Comparison.
A device or program used to generate keys is called a key generator or keygen.
Generation in cryptography[edit]
Modern cryptographic systems include symmetric-key algorithms (such as DES and AES) and public-key algorithms (such as RSA). Symmetric-key algorithms use a single shared key; keeping data secret requires keeping this key secret. Public-key algorithms use a public key and a private key. The public key is made available to anyone (often by means of a digital certificate). A sender encrypts data with the receiver's public key; only the holder of the private key can decrypt this data.
Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation Download
Since public-key algorithms tend to be much slower than symmetric-key algorithms, modern systems such as TLS and SSH use a combination of the two: one party receives the other's public key, and encrypts a small piece of data (either a symmetric key or some data used to generate it). The remainder of the conversation uses a (typically faster) symmetric-key algorithm for encryption.
Computer cryptography uses integers for keys. In some cases keys are randomly generated using a random number generator (RNG) or pseudorandom number generator (PRNG). A PRNG is a computeralgorithm that produces data that appears random under analysis. PRNGs that use system entropy to seed data generally produce better results, since this makes the initial conditions of the PRNG much more difficult for an attacker to guess. Another way to generate randomness is to utilize information outside the system. veracrypt (a disk encryption software) utilizes user mouse movements to generate unique seeds, in which users are encouraged to move their mouse sporadically. In other situations, the key is derived deterministically using a passphrase and a key derivation function.
Many modern protocols are designed to have forward secrecy, which requires generating a fresh new shared key for each session.
Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation 1
Call of duty 5 cd key generator download 2016. Classic cryptosystems invariably generate two identical keys at one end of the communication link and somehow transport one of the keys to the other end of the link.However, it simplifies key management to use Diffie–Hellman key exchange instead.
The simplest method to read encrypted data without actually decrypting it is a brute-force attack—simply attempting every number, up to the maximum length of the key. Therefore, it is important to use a sufficiently long key length; longer keys take exponentially longer to attack, rendering a brute-force attack impractical. Currently, key lengths of 128 bits (for symmetric key algorithms) and 2048 bits (for public-key algorithms) are common.
Generation in physical layer[edit]
Wireless channels[edit]
A wireless channel is characterized by its two end users. By transmitting pilot signals, these two users can estimate the channel between them and use the channel information to generate a key which is secret only to them.[1] The common secret key for a group of users can be generated based on the channel of each pair of users.[2]
Optical fiber[edit]
A key can also be generated by exploiting the phase fluctuation in a fiber link.[clarification needed]
See also[edit]
Part 2 Pairing Method And Key Generation 3
- Distributed key generation: For some protocols, no party should be in the sole possession of the secret key. Rather, during distributed key generation, every party obtains a share of the key. A threshold of the participating parties need to cooperate to achieve a cryptographic task, such as decrypting a message.
References[edit]
- ^Chan Dai Truyen Thai; Jemin Lee; Tony Q. S. Quek (Feb 2016). 'Physical-Layer Secret Key Generation with Colluding Untrusted Relays'. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications. 15 (2): 1517–1530. doi:10.1109/TWC.2015.2491935.
- ^Chan Dai Truyen Thai; Jemin Lee; Tony Q. S. Quek (Dec 2015). 'Secret Group Key Generation in Physical Layer for Mesh Topology'. 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). San Diego. pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/GLOCOM.2015.7417477.